Bermed Houses - Ultimate Guide to Energy Efficiency, Design, and Benefits
Bermed houses are a fantastic example of sustainable architecture, naturally blending into the landscape while delivering outstanding energy efficiency.
These Earth-sheltered homes aren’t just about innovative design—they’re perfect for anyone looking for eco-friendly living spaces that truly connect with the environment.

What Are Bermed Houses?
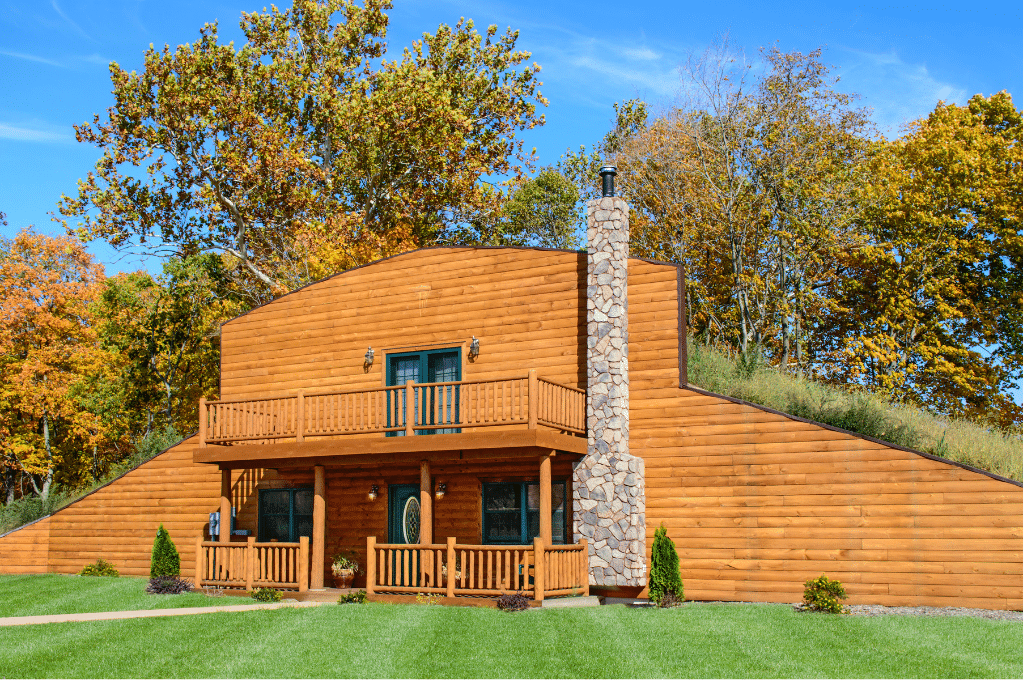
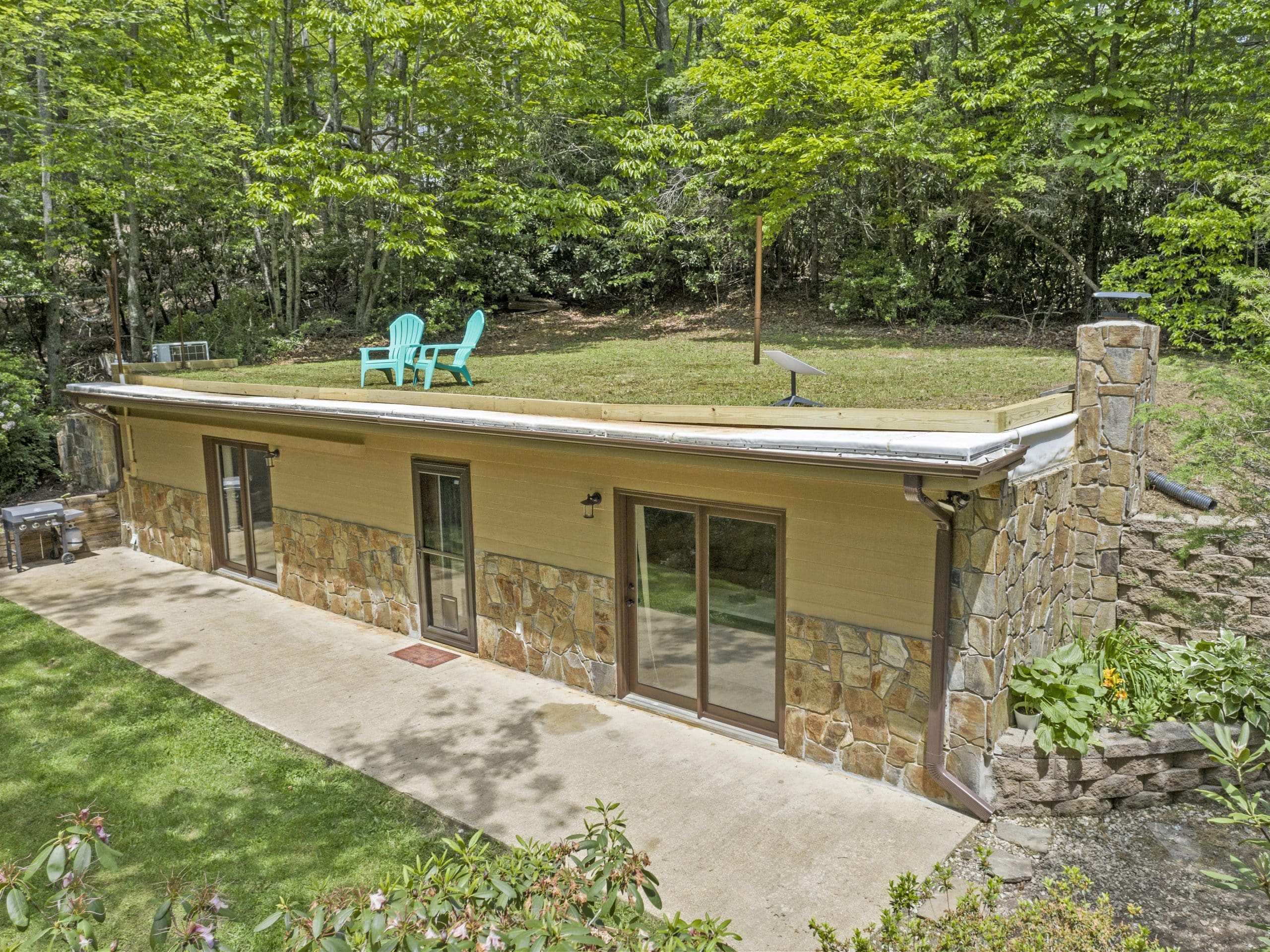
At their core, bermed houses are structures that are partially covered with earth, typically on three sides. This integration with the land provides natural insulation, shielding the home from extreme temperatures and external elements. The concept of Earth-sheltered homes isn’t novel; ancient civilizations recognized the benefits of building into the ground, using the Earth’s mass for protection and stability. Today, with a resurgence in sustainable living and green building practices, bermed houses are gaining traction among environmentally conscious homeowners.
Key Features of Bermed Houses
Berming involves piling earth against the exterior walls of a structure. This earth acts as a thermal mass, regulating indoor temperatures by absorbing and slowly releasing heat. Common materials used in constructing these homes include reinforced concrete for structural integrity, coupled with high-quality insulation to prevent moisture intrusion and ensure comfort. One of the standout features of bermed houses is their ability to blend with the landscape. By integrating the home into the terrain, architects achieve a harmonious design that minimizes visual impact and promotes landscape integration.
Advantages of Bermed Houses
The energy efficiency of bermed houses is unparalleled. Their design naturally reduces heating and cooling costs, thanks to the insulating properties of the surrounding earth. Additionally, these homes offer robust protection against elements like wind, fire, and even earthquakes. Their earth-covered exteriors shield them from harsh weather, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance. For homeowners, this translates to long-term savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Site Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right location is paramount when considering a bermed house. Ideal sites have stable soil types, gentle slopes for optimal drainage, and favorable orientations to maximize passive solar design benefits. Before construction, thorough site preparation is essential. This includes assessing soil stability, ensuring proper drainage to prevent moisture accumulation, and implementing waterproofing measures to protect the structure.
Architectural Design Considerations
Designing a bermed house requires balancing functionality and aesthetic appeal. Architectural principles specific to Earth-sheltered homes emphasize the importance of natural lighting and ventilation. Since three sides are typically covered with earth, an exposed facade becomes crucial for windows and doors. Common design styles include U-shape and L-shape layouts and atrium designs that incorporate open central spaces to flood interiors with light. Integrating features like skylights and sun tunnels can further enhance natural illumination.
Construction Process for Bermed Houses
Constructing a bermed house is a meticulous process. It begins with laying a strong foundation, often using reinforced concrete. Once the primary structure is in place, insulation and moisture barriers are added to prevent water ingress and ensure thermal efficiency. The surrounding earthEarthhen carefully piled against the walls, providing stability and proper compaction. Embracing sustainable practices, many builders opt for natural materials and recycled resources, enhancing the home’s eco-friendly credentials.
Cost Considerations
While the initial construction costs of bermed houses might be higher than traditional homes, averaging around $150 to $200 per square foot, the long-term savings are substantial. Factors influencing cost include location, chosen materials, and design complexity. However, homeowners often find that reduced energy bills and minimal maintenance expenses offset the upfront investment.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Bermed houses are champions of energy efficiency. The thermal mass provided by the Earth ensures that indoor temperatures remain stable, reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling. Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels positioned on exposed facades or roofs, can further diminish energy consumption. Geothermal heating systems, tapping into the Earth’s constant temperatures, are also popular choices, enhancing the home’s sustainable profile.
Comfort and Interior Environment
Living in a bermed house offers a unique comfort level. The natural insulation ensures a consistent indoor climate, shielding inhabitants from external temperature fluctuations. Additionally, the earth-covered walls provide excellent noise reduction, creating a serene indoor environment.
With strategic window placement and ventilation systems, homeowners can enjoy abundant natural light and fresh air, ensuring a healthy living space.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their numerous benefits, bermed houses come with challenges. Limited window space due to earth coverage can restrict views and natural light. Initial construction costs might deter some potential homeowners. Additionally, navigating building permits and local regulations can be complex, given the unconventional nature of Earth-sheltered homes. However, these challenges can be effectively addressed with expert consultation and innovative design solutions.
FAQs About Bermed Houses
What is the lifespan of a bermed house?
Bermed houses are built for longevity, often lasting several decades. Their protected structure minimizes wear and tear, resulting in less maintenance than traditional homes.
Are bermed houses safe in extreme weather?
Absolutely. The earth’s coverage protects against extreme weather conditions, including storms, high winds, and wildfires.
How does a bermed house differ from an underground house?
While both are Earth-sheltered, a bermed house is partially covered with earth, typically on three sides, whereas an underground house is completely buried beneath the surface.
Can you add windows to a bermed house?
Yes. Strategic window placement ensures natural light and ventilation without compromising the home’s energy efficiency. Features like skylights can also enhance interior illumination.
The Future of Bermed Houses
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, the appeal of sustainable and energy-efficient homes is undeniable. Bermed houses, with their blend of innovative design and environmental harmony, are poised to become a mainstream choice in residential architecture. For those seeking a home that offers comfort, durability, and eco-friendly benefits, exploring bermed house designs and consulting with experts can be a rewarding endeavor.
Embracing such sustainable architecture not only benefits homeowners but also contributes positively to the planet.